Genetic variation in the HLA class II region is the strongest genetic association with MS, yet the mechanisms linking HLA alleles to disease remain incompletely understood.
Using human HLA class II transgenic mice, we identified encephalitogenic epitopes of myelin antigens (e.g., PLP in HLA-DR3 and MOG in HLA-DR2) and demonstrated allele-dependent differences in T-cell responses and disease susceptibility. We also discovered that HLA alleles shape gut microbiome composition, and that these microbiome differences modulate mucosal and CNS immune tone. For example, HLA-DQ8 synergizes with HLA-DR3 to worsen disease through IL-17–driven inflammation, while distinct HLA backgrounds produce differential microbial communities that influence disease severity.
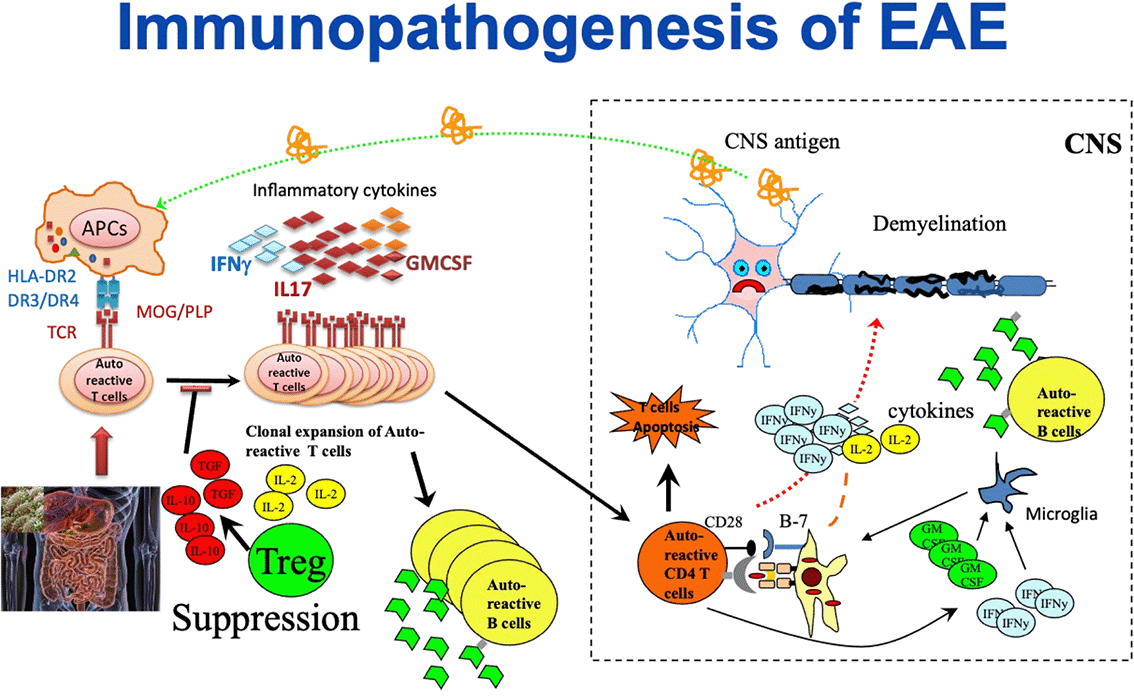
Key Findings & Interpretation
- HLA class II alleles determine which myelin epitopes become pathogenic, influencing T-cell repertoire and neuroinflammation.
- HLA-DQ8 synergizes with HLA-DR3 to increase EAE severity via enhanced IL-17–mediated inflammatory responses.
- HLA class II polymorphisms alter gut microbiome composition, demonstrating that genetics influence microbial ecology.
- These allele-specific microbiome differences are functionally meaningful, contributing to changes in disease severity and CNS inflammatory profiles.
- Together, these findings reveal a genetics → microbiome → immune response axis central to MS pathogenesis.
Future Directions
- Dissect microbiome-dependent vs. microbiome-independent immune pathways regulated by specific HLA alleles.
- Identify microbial taxa and metabolites that interact with HLA-restricted T-cell responses to drive or suppress disease.
- Develop HLA-tailored microbiome or metabolic interventions to promote tolerance and reduce neuroinflammation in genetically susceptible individuals.
Selected Publications
Mangalam AK, Khare M, Krco C, Moses R, and David C (2004). Identification of T cell epitopes on human proteolipid protein and induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in HLA class II-transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol. 34:280-290. PMID: 14971054
Mangalam A, Luckey D, Basal E, Jackson M, Smart M, Rodriguez M, and David C (2009). HLA-DQ8 (DQB1*0302) Restricted Th17 cells Exacerbates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in HLA-DR3 Transgenic Mice. J Immunol. 182:5131-39. PMID: 19342694
Mangalam AK, Luo N, Luckey D, Papke L, Hubbard A, Wussow A, Smart M, Giri S, Rodriguez M, David C (2014). Absence of IFN-γ increases brain pathology in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-susceptible DRB1*0301.DQ8 HLA transgenic mice through secretion of proinflammatory cytokine IL-17 and induction of pathogenic monocytes/microglia into the central nervous system. J Immunol. 193(10):4859-70. PMID: 25339670.
Shahi SK, Ali S, Jaime C, Guseva N, and Mangalam AK, (2021). HLA class II polymorphisms modulate gut microbiota and EAE phenotype. Immunohorizons. 5, 627-646. DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2100024 PMID: 34380664 PMCID: PMC8728531